A concussion is a traumatic brain injury that affects your brain function. Effects are usually temporary but can include headaches and
problems with concentration, memory, balance and coordination.
Concussions are usually caused by a blow to the head. Violently shaking of the head and upper body also can cause concussions
What is a Concussion
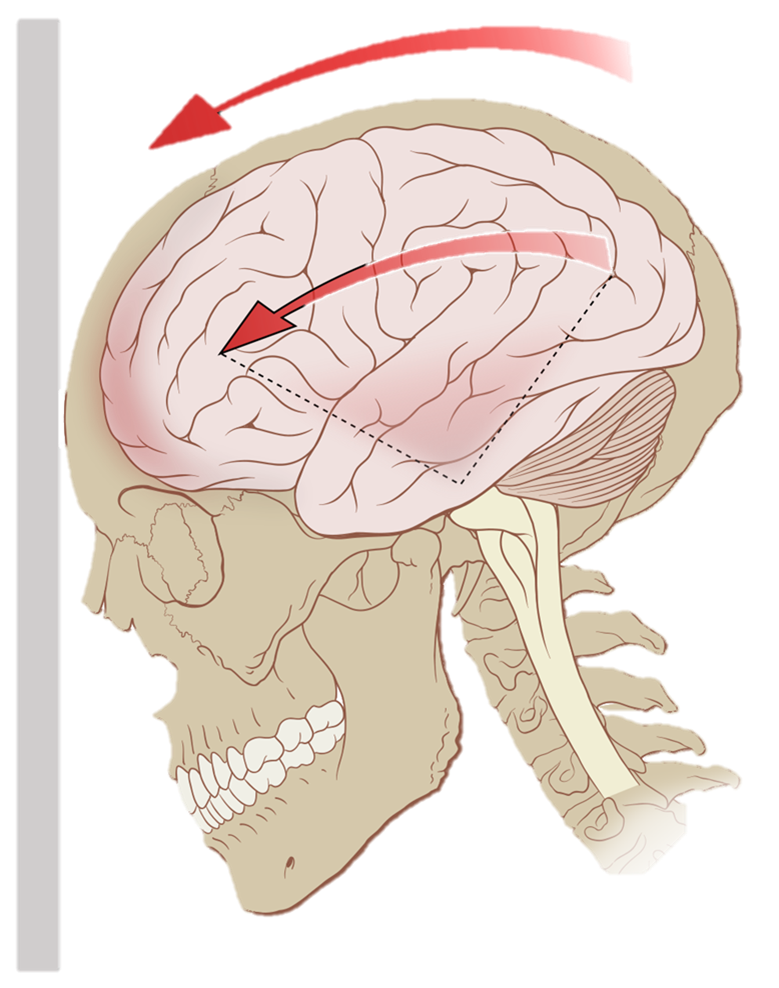
Your brain has the consistency of gelatin. It’s cushioned from everyday jolts and bumps by cerebrospinal fluid inside your skull.
A violent blow to your head and neck or upper body can cause your brain to slide back and forth forcefully against the inner walls of your skull.
Sudden acceleration or deceleration of the head, caused by events such as a car crash or being violently shaken, also can cause brain injury.
These injuries affect brain function, usually for a brief period, resulting in signs and symptoms of concussion.
This type of brain injury may lead to bleeding in or around your brain, causing symptoms such as prolonged drowsiness and confusion.
These symptoms may develop immediately or later.Such bleeding in your brain can be fatal.
That’s why anyone who experiences a brain injury needs monitoring in the hours afterward and emergency care if symptoms worsen.
Symptoms
Signs of a concussion usually appear within a few minutes or hours of a head injury. But occasionally they may not be obvious for a few days, so it’s important to look out for any problems in the days following.
- A headache that does not go away or is not relieved with painkillers.
- Dizziness
- Feeling or being sick
- Memory loss – you may not remember what happened before or after the injury.
- Clumsiness or trouble with balance.
- Unusual behaviour – you may become irritated easily or have sudden mood swings.
- Feeling stunned, dazed or confused.
- Changes in your vision – such as blurred vision, double vision or “seeing stars”
- Being knocked out or struggling to stay awake
Treatment
- Things you can do to help your recovery include:
- Getting plenty of rest and avoiding stressful situations
- Asking someone to stay with you for the first 48 hours
- Taking paracetamol or ibuprofen if you have a headache – do not take aspirin because it could cause your injury to bleed
- Avoiding alcohol
- Gradually increasing how much activity you do each day
- Avoiding sports or strenuous exercise for at least a week, and avoiding contact sports for at least 3 weeks
Prevention
Wearing the recommended equipment when taking part in a contact sport.
Making sure any contact sport you or your child are taking part in is supervised by a properly qualified and trained person
Wearing a seatbelt when driving
Wearing a helmet when riding a motorcycle, bicycle or horse
It’s important to avoid head injuries as repeated concussions or blows to the head have been linked to serious problems, including a brain condition called chronic traumatic encephalopathy.
Contact Me
Let's chat!
Need more information? Send me an email or drop me a line. I don’t bite!
- Charlotte@rehabontheroad.co.uk
- 07971448719